Interferometric Surveys
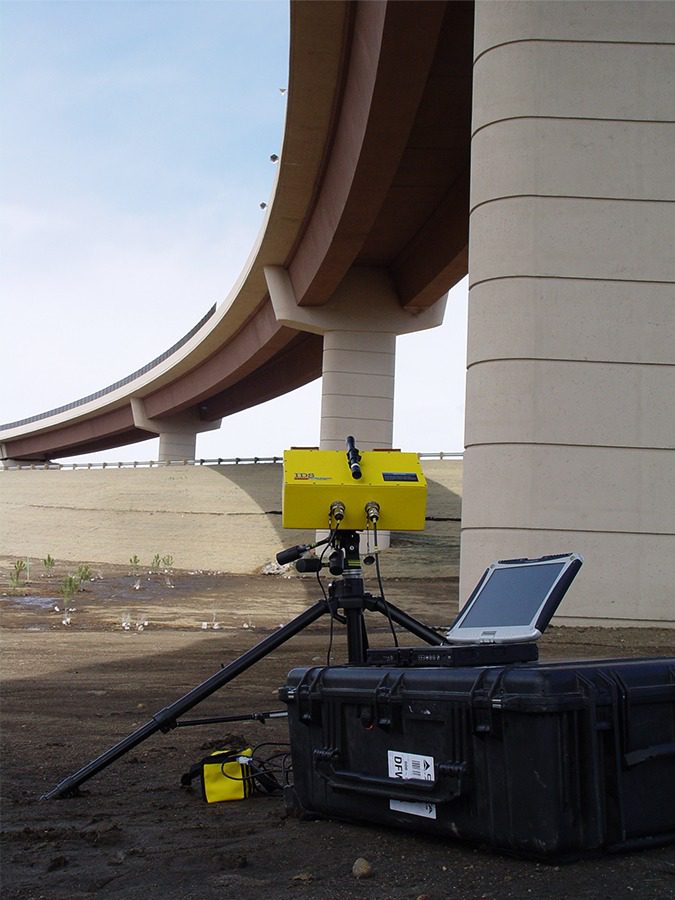

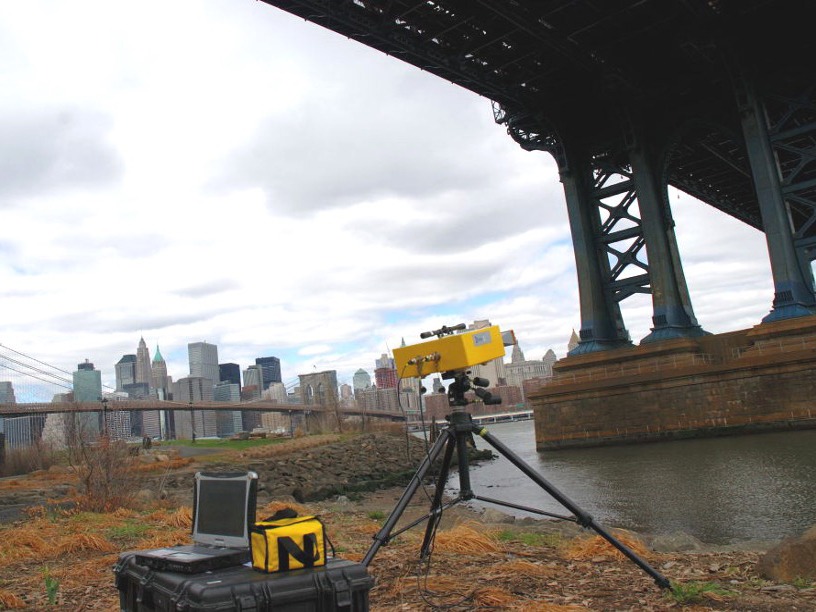
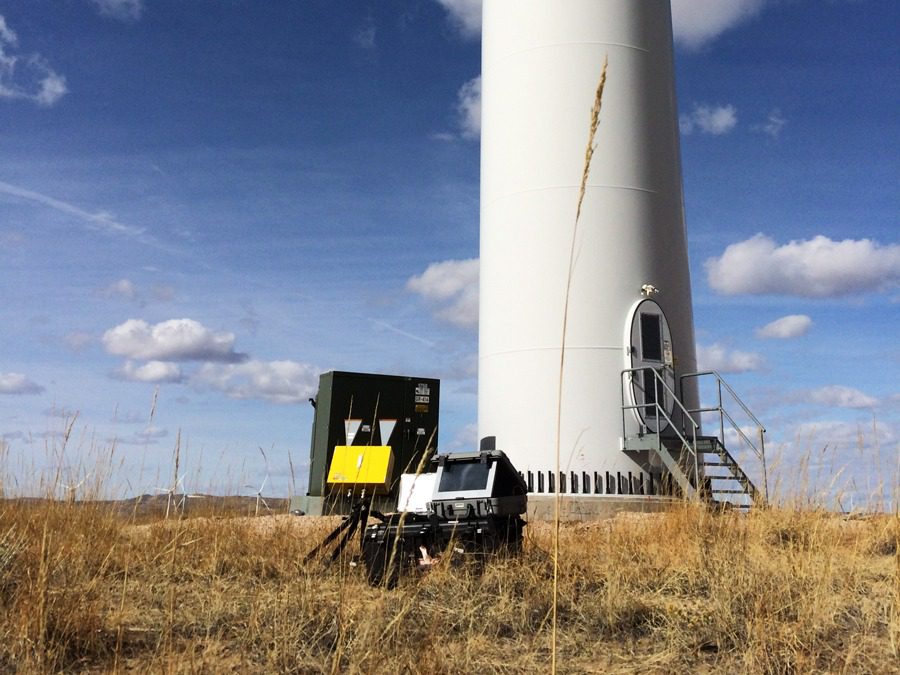
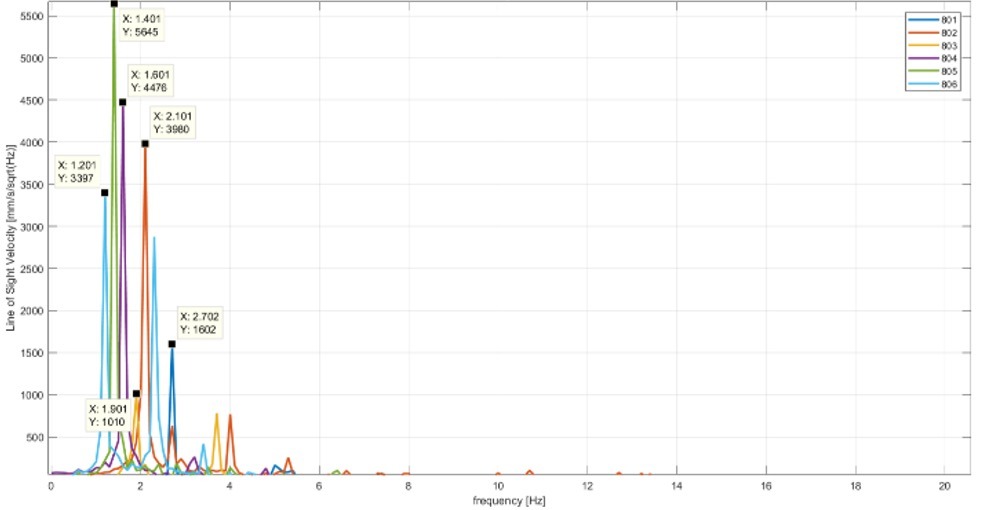
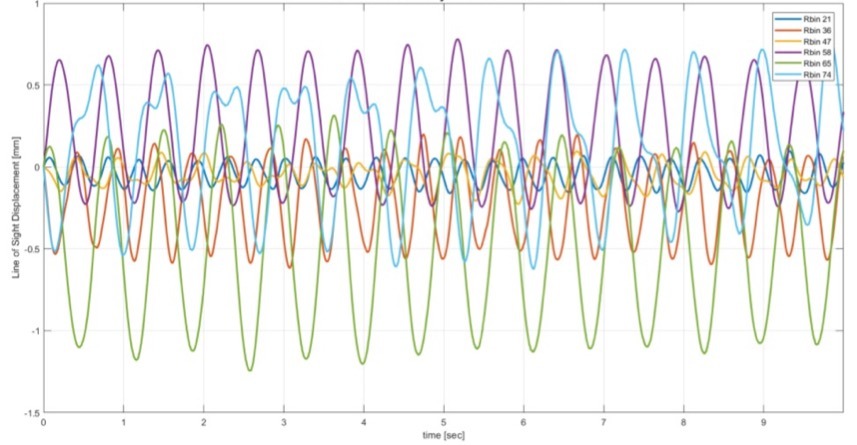
Olson Engineering has the equipment and expertise to offer remote monitoring by interferometric radar to measure movements in bridges, structures, ports and concrete/masonry dams. Static monitoring services include structural load testing, structural displacement and collapse hazards, and preservation of historic buildings.
Dynamic services include structural resonance frequency measurement, structural modal shape analysis, and monitoring of deformation. Olson Engineering owns both IBIS-S and IBIS-L equipment to carry out Imaging by Interferometric Surveys (IBIS).
Applicable on:
- Bridges
- Buildings
- Structures
- Port Facilities
Test for:
- Displacement
- Deformation
- Vibration
- Response to Static and Dynamic Load

Image Gallery

All Methods